中文
ENGLISH
中文
ENGLISH
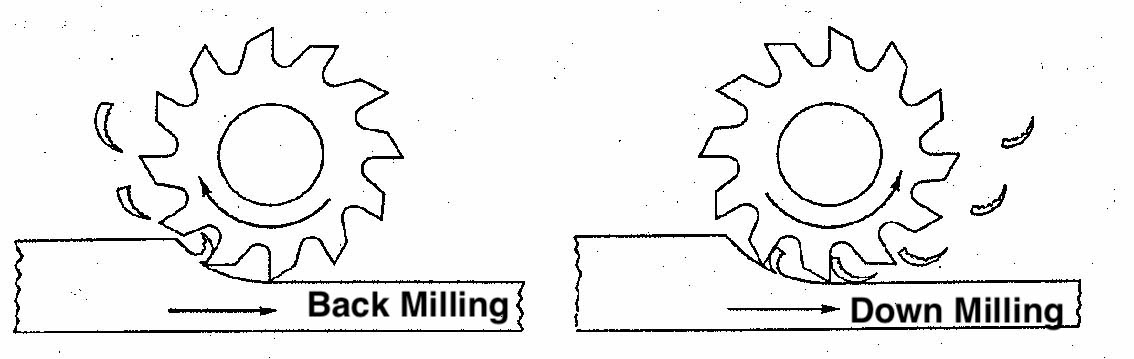
What’s Back Milling?
Also called up vowin.cn/en/News/news1251.html' target='_blank'>milling. It is a traditional vowin.cn/en/News/news1251.html' target='_blank'>milling method, the principle of which is to rotate the tool in the opposite direction of the workpiece, so as to produce upward cutting force. In this cutting process, when the tool engages, it is forced to confront the working parts, creating relatively high friction, and thus generating more heat. Milling up, on the other hand, is the opposite of milling down. As the cutter begins to subtract the smallest material, it gradually cuts the largest material because it rotates.
The advantages of Back Milling
1. The reaction force in this machining method can eliminate the error caused by the machine rebound.
2. It is the preferred method of rough machining and can meet the working parts of ductile and brittle materials (e.g., hardening, casting, or forging).
3. Back milling can cut thin walls and extended surfaces. The reason for this is that the deflection is minimized due to the reaction force during cutting.
What’s Down Milling?
Also known as climbing milling. It is the same direction of tool rotation on the workpiece, resulting in a downward cutting force. The meshing of the knife with the workpiece at the entrance will cut out the maximum material and then gradually reach zero as the knife rotates. Having the same direction of action has less resistance, which may mean less heat is generated during processing.
The advantages of Down Milling
1.It reduces the load from the cutting edge, which reduces tool wear and prolongs tool life.
2.It produces less heat than back milling.
3.The way it is cut (from thick to thin) produces a smooth surface finish.
4.Simple working jig can be used.
5.It has better chip evacuation heat.