中文
ENGLISH
中文
ENGLISH
The method of producing blanks or parts by pouring liquid metal into a moulding cavity having a shape identical to the shape and size of the part and leaving them to cool down for solidification, is generally called the forming or casting of liquid metal.
Processing flow: Liquid metal –> vowin.cn/' target='_blank'>mold filling –> solidification & contraction –> casting
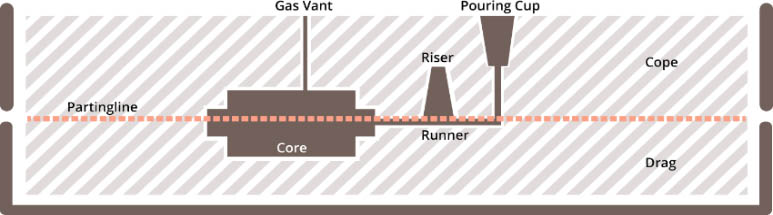

A method of producing casting in sand molds. Steel, iron and most nonferrous alloy castings can be obtained via sand casting method.
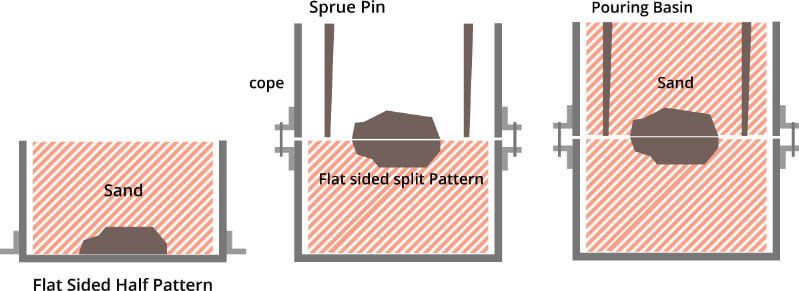
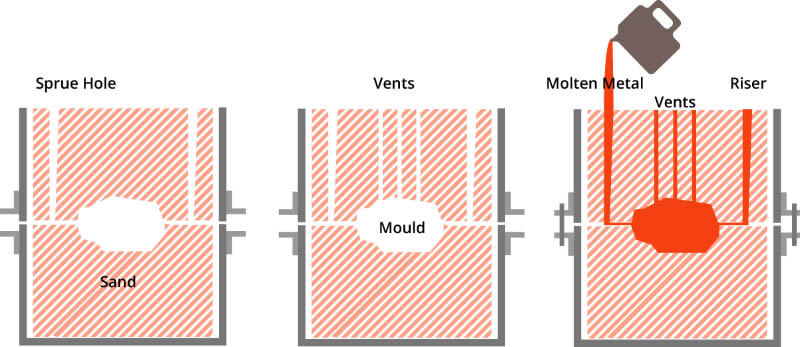
Application: Engine cylinder block, cylinder head, cranks and other castings used for automobiles.

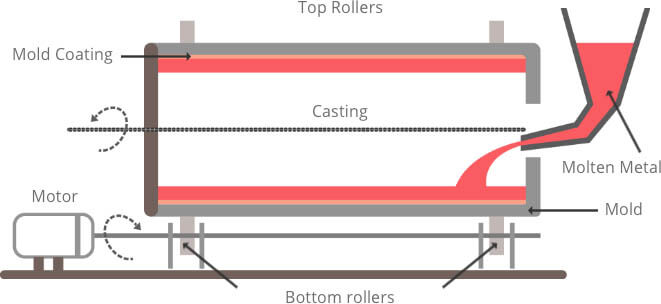
Investment Casting
A casting scheme, which is often called “dewaxing casting”, that uses fusible material to make a pattern, on which several layers of refractory material are applied to produce a shaping shell, from which the pattern is melted to obtain an integral casting mold that will be baked at high temperature and can be used for casting via sand filling.
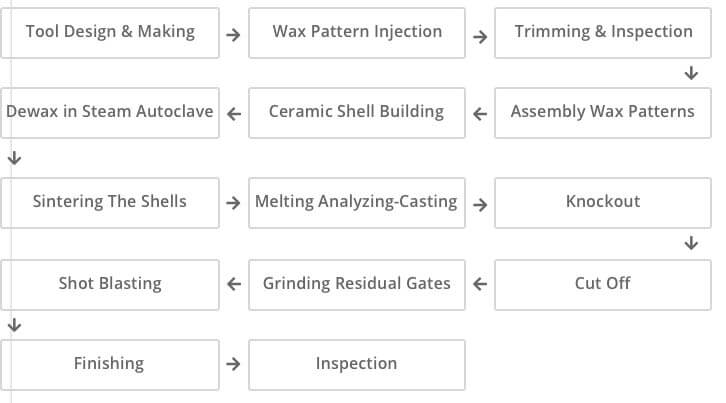
1. Complicated procedures and higher cost.
Applications Applicable to produce small parts with complicated contours and high precision, or that cannot be manufactured in other ways, such as blades of turbo engine.

Die Casting
Metal liquid under high pressure is pressed at high speed into the cavity of a precise metallic mold, in which the metal liquid under pressure is cooled down and solidifies into the casting.
Processing advantages
Application Die casting was initially used for the automobile and instrument industries and then spread to other sectors, such as agricultural machinery, machine tool, electronics, national defense, computer, medical devices, watches and bells, camera and daily hardware.

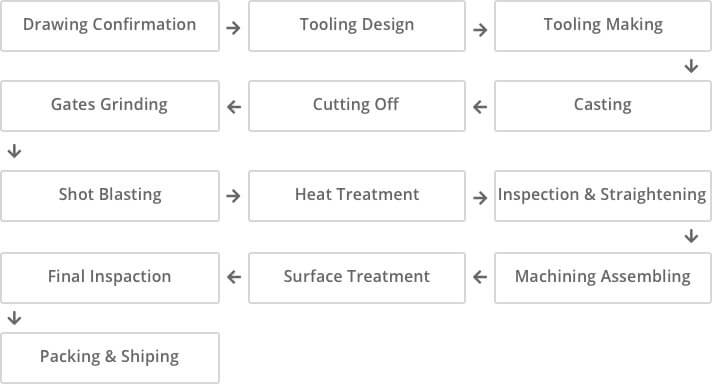
Low Pressure Casting
It is a method of producing casting via crystallization under pressure after liquid metal is filled in the die mold under a relative low pressure (0.02~0.06MPa).
Application It is mainly focused on traditional products (cylinder head, hub and cylinder rack).

Centrifugal Casting
A method of pouring metal liquid into a rotating casting mold so as to fill the mold with centrifugal force and solidify the metal into desired shapes.
Processing advantages
Processing disadvantages
Application Centrifugal casting was used for producing cast tubes in early time. It is used to manufacture steel, iron and nonferrous carbon alloy castings used in the metallurgy, mining, traffic, drainage and irrigation machinery, aviation, national defense, automobile and other industries. It is most commonly used for manufacturing castings such as centrifugal cast tubes, cylinder liners and shaft sleeves used for internal combustion engines.

Gravity die casting
A method of forming castings by filling a metallic mold with liquid metal under gravity and solidifying it in the mold.
Processing flow:
Processing advantages
Processing disadvantages
Application Metallic mold is applicable to batch producing either nonferrous alloy castings, such as aluminum alloy and magnesium alloy parts with complicated shapes, or steel and iron castings or ingots.

Vacuum die casting
An advanced die casting process that is used to improve the mechanical property and surface quality of casting by removing gas from the die casting mold cavity or considerably reducing the porosity or dissolved gas in the casting.
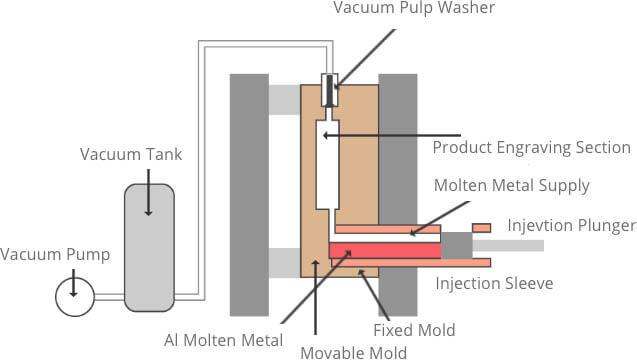
Processing disadvantages

Squeezing Die Casting
A method of directly obtaining the part or blank from liquid or half-solid metal that solidifies or flow to form under high pressure. It is a metal-forming technique with potential prospect for application due its high liquid metal utilization, simplified procedure and stable quality.
Processing flow:
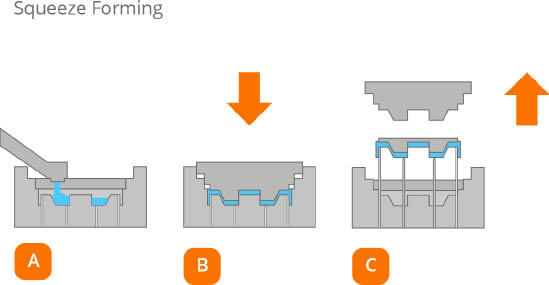
coating spray, pouring alloy, mold closing, pressurizing, pressure keeping, pressure releasing, mold opening, blank demoulding, reset.
Indirect squeezing die casting: Coating spray, mold closing, feeding, filling, pressurizing, pressure keeping, pressure releasing, mold opening, blank demoulding, reset.
Technical features
Application It can be used to produce a variety of alloys, such as aluminum alloy, zinc alloy, copper alloy and nodular cast iron.

Lost foam casting also known as full mold process. An innovative casting method that uses wax or foam models in a shape and size similar to the casting to form a group of models via bonding, which are applied with refractory coating and then dried with heat, buried in dry quartz sand to form via vibration, and that liquid metal is poured under negative pressure to gasify the models so that liquid metal takes the position of model, and cools down and solidifies to form the casting.
Processing flow:
Pre-foaming -> Foam molding -> dipping in paint arrow-right drying -> shaping -> pouring -> shakeout -> clearing
Technical features
Application It is suitable for production of precise castings with complicated structure, in various sizes, without limitation to alloy species and batches of production, such as gray pig iron engine housing and high manganese steel elbow.

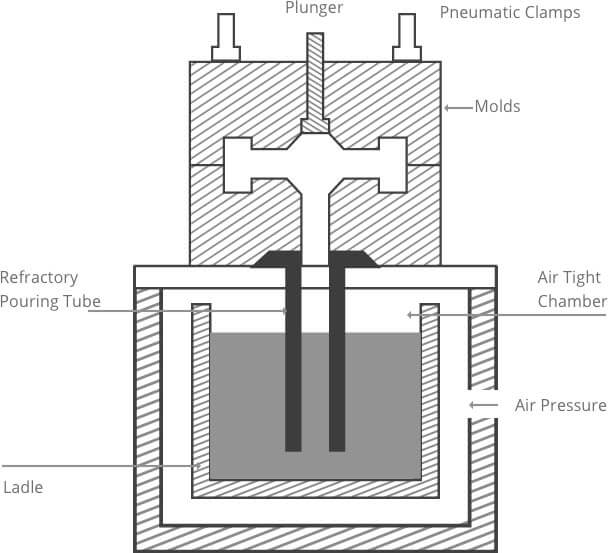
Continual Casting
Continual Casting This is an advanced casting method. Its principle is that molten metal is continuously poured into a special metallic mold called crystallizer, from which the solidified (skulled) casting is continuously pulled out from the other end of the crystallizer, and it is possible to obtain a casting with any or certain length.
Processing flow:
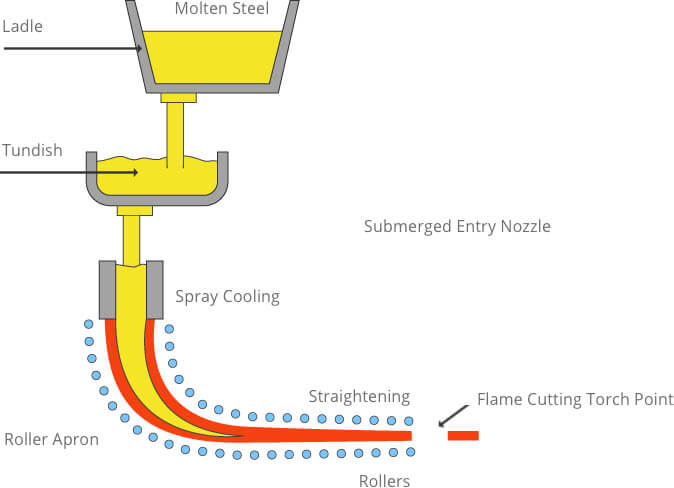
Technical features
Application Continual casting method can be used to cast steel, iron, copper alloy, aluminum alloy and magnesium alloy into long castings with consistent form of section, such as ingot, plate blank, stick blank and pipe.
Plastic forming: It is a method of using the plasticity of material to manufacture a part with the external force from tools and mold so as to reduce or eliminate cutting. It includes a variety of techniques, such as forging, rolling, extruding, drawing and punching.

This is a processing method that uses a kind of forging machine to impose pressure on metallic blank so as to obtain plastic deformation in order to achieve a casting with certain mechanical property, shape and size
According to the forming mechanism, forging can be divided into free forging, die forging, grinding ring and special forging.
According to the forming mechanism, forging can be divided into free forging, die forging, grinding ring and special forging.
Mold forging It is formed with a mold on a mold hammer or hot die forging press.
Grinding ring It is referred to the use of special equipment ring rolls to manufacture ring parts with different diameters. Such method can also be used to manufacture auto hub, train wheel hub and other ring parts.
Special forging It includes rolling forging, cross wedge rolling, radial forging, liquid forging and other forging methods, which are suitable for manufacturing some parts with special shapes.
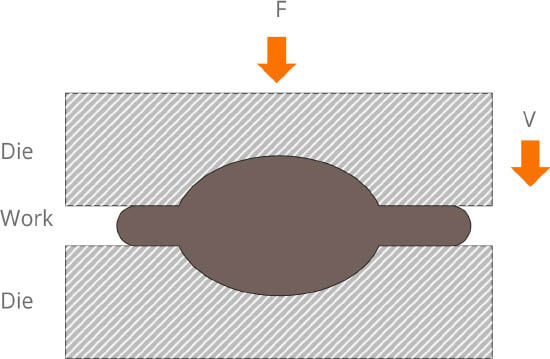
Processing flow
Blank heating -> rolling to prepare blank -> die forging -> cutting the edges -> punching -> rectifying -> intermediate inspection -> heat treatment of forged piece -> clearing -> rectifying -> inspection
Application Rolls and herringbone gears of heavy mills; rotors, blades and retaining rings of steam turbine generator unit; working cylinder and column of large hydraulic press; locomotive axle; crankshaft and connecting rod of automobiles or tractors.

A processing method that forces metal blank to pass between a pair of rotary rolls (in various shapes) to reduce material section and increase its length due to compression of the rolls.
Rolling category Axial rolling, cross rolling and skew rolling according to movement of the rolled piece.
Axial rolling: The process in which metal passes and deforms plastically between a pair of rolls that rotate in opposite directions.
Cross rolling: The rolled piece after deformation moves in the same direction with the axis of the rolls.
Skew rolling: The piece under rolling moves helically and it forms a non-special angle with axis of the roll.
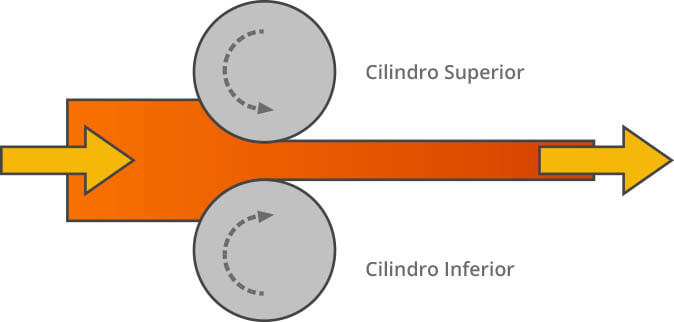
Application It is mainly used for metallic section materials, plates or tubes, and some nonmetal products such as plastics and glass.

A processing method that is used to acquire desired product by extruding the blank, under non-uniform stress in three directions, through a slot or gap so as to reduce its section and increase its length. Such processing of blank is called extruding forming.
Processing flow
Preparation before extruding -> cast rod heating -> extruding -> stretching, twisting and straightening -> sawing (sizing) -> sampling for inspection -> man-hour efficiency -> packing and warehousing piece -> clearing -> rectifying -> inspection
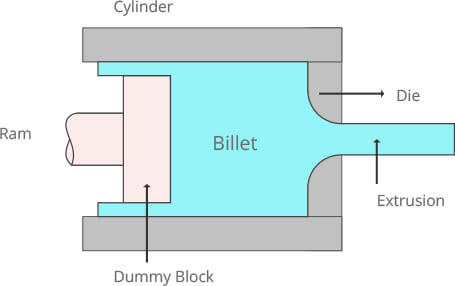
Processing disadvantages
Applicable scope of production It is mainly used for manufacturing parts with long stick, deep hole, thin wall or special sections.

A processing method that utilizes the plasticity of metal to acquire products with appropriate shapes and sizes by applying force to one end of the metal and pull the metal blank through a die hole whose section is smaller than that of the metal blank.
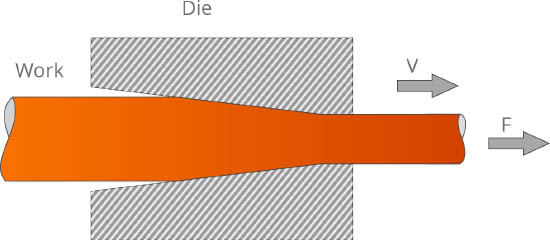
Processing advantages
Processing disadvantages
Applicable scope of production It is a primary method of drawing metal tubes, bars, sectional material and wire rods.

Punching: A processing method that applies external force to the plate, strip, tube or sectional material with the help of press and mold to achieve plastic deformation or separation in order to obtain desired shape or size of a work-piece (stamping).
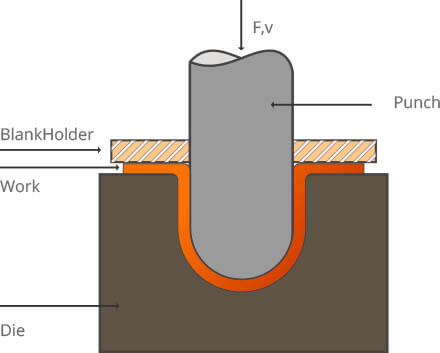
Applicable scope of production Of the steels produced in the world, nearly 60-70% are plates, most of which are finished through stamping, including body, chassis, fuel tank and radiator of cars; steam pocket of boiler; container housing; motor; iron core and silicon steel sheet of electric appliances. There are also lots of stamping used in instrument and apparatus, home appliances, bicycles, office equipment, and utensils used in daily life.

A manufacturing process in which the part is processed by using a knife to directly cut off extra thickness of metal from the blank in order to achieve the size accuracy, shape and mutual positioning precision, surface quality and other technical requirement of the drawings.
Suppliers of machining equipment Mikron and Bumotec of switsland, DMG and Hermle of Germany, Mori Seiki, Okuma, Mazak and Makino of Japan, MAG and Hardinge Bridgeport of the United States, Italian Fidia, Spanish Danobat, Hardinge and Haas of the United States, Doosan, Hyundai and Samsung of South Korea, Yeongchin, Tong-Tai and Dick Lyons of Taiwan, BYJC, BMEIMT, TONMAC, Shenyang, Shinri, Neway, Rifa, Haitian, Dajin.

Welding: Welding is also known as fusion. It is a manufacturing process and technique that splices metal or other plastic materials (such as plastics) with heating, high temperature or high pressure.

A processing technique that is used to make metallic materials, composite materials and various products with metal or metal powder (or mixture of metal powder and nonmetal powder) as raw material by forming and sintering. Welding: Welding is also known as fusion. It is a manufacturing process and technique that splices metal or other plastic materials (such as plastics) with heating, high temperature or high pressure.
Basic processing flow
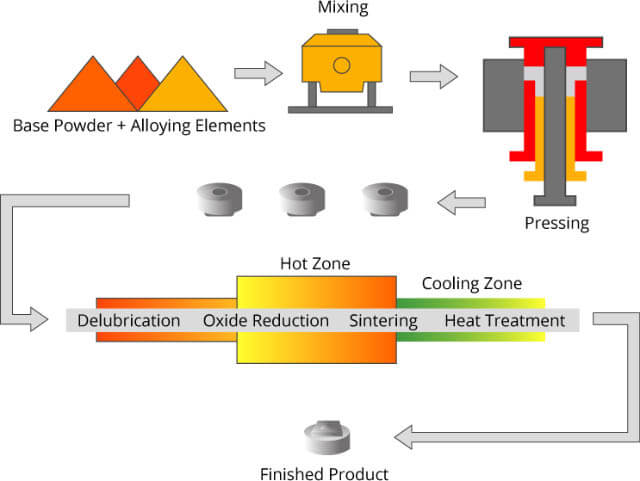
Processing advantages
Processing disadvantages
Applicable scope of production With powder metallurgy, it is possible to directly manufacture porous, half-dense or full-dense materials and products, such as oily bearing, gear, cam, guide rod and cutting tools.

SSM for short. The unique rheological property and stirring fusibility of SSM can be used to control casting quality.
Semi-solid forming can be divided into Rheoforming and Thixoforming.
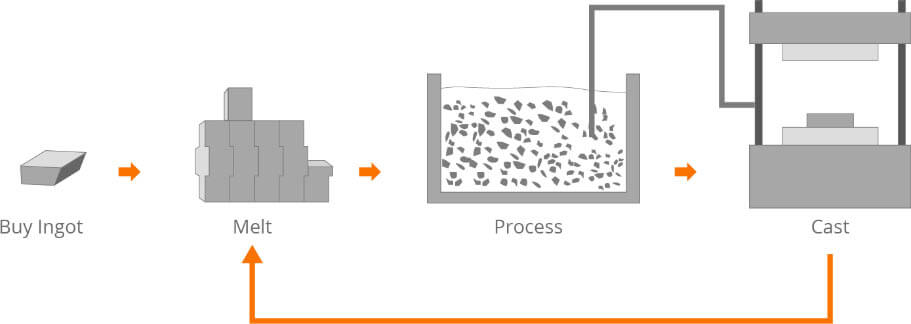
Technical features
Application Currently, it has been successfully used for the primary cylinders, steering system parts, rocker arm, engine pistons, wheel hubs, drive system parts, fuel system parts and air conditioner parts in aviation, electronics and consumer goods.


